** 이 글은 ' 면접을 위한 cs 전공지식 노트 ' 책을 기반으로 정리한 글 입니다 **
🙋🏻♀️ 팩토리 패턴
- 객체를 사용하는 코드에서 객체 생성 부분을 떼어내 추상화한 패턴
- 상속관계에 있는 두 클래스에서 상위 클래스가 중요한 뼈대를 결정 & 하위 클래스가 객체 생성에 관한 구체적 내용 결정
/* Online Java Compiler and Editor */
abstract class Coffee{ /*상위 추상 클래스*/
public abstract int getPrice();
@Override
public String toString(){
return "Hi this coffee is " + this.getPrice();
}
}
class CoffeeFactory{ /* 객체 생성 클래스 -> factory */
public static Coffee getCoffee(String type, int price){
if("Latte".equalsIgnoreCase(type)) return new Latte(price);
else if("Americano".equalsIgnoreCase(type)) return new Americano(price);
else{
return new DefaultCoffee();
}
}
}
class DefaultCoffee extends Coffee{
private int price;
public DefaultCoffee(){
this.price = -1;
}
@Override
public int getPrice(){
return this.price;
}
}
class Latte extends Coffee {
private int price;
public Latte(int price){
this.price=price;
}
@Override
public int getPrice() {
return this.price;
}
}
class Americano extends Coffee {
private int price;
public Americano(int price){
this.price=price;
}
@Override
public int getPrice() {
return this.price;
}
}
public class HelloWorld{
public static void main(String []args){
Coffee latte = CoffeeFactory.getCoffee("Latte", 4000);
Coffee ame = CoffeeFactory.getCoffee("Americano",3000);
System.out.println("Factory latte ::"+latte);
System.out.println("Factory ame ::"+ame);
}
}
😃 팩토리 패턴 장점
- 상하위 클래스의 느슨한 결합
- 객체 생성 로직 분리로 코드 리팩터링에 좋음 ( 유지 보수성 ⬆️ )
🙋🏻♀️ 전략 패턴 ( Strategy Pattern ) = 정책 패턴
- 객체의 행위를 바꾸고 싶은 경우, 직접 수정하지 않고 전략이라고 부르는 캡슐화한 알고리즘을 컨테스트 안에서 바꿔주면서 상호 교체 가능하게 하는 패턴
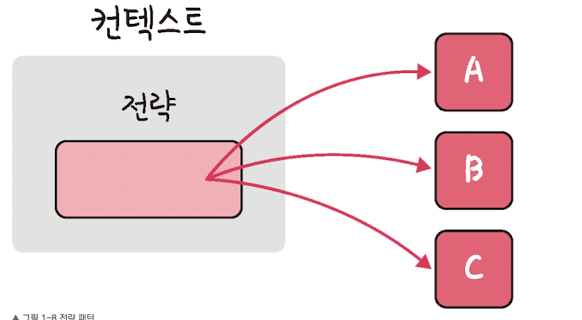
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
interface PaymentStrategy {
public void pay(int amount);
}
class KAKAOCardStrategy implements PaymentStrategy { // 전략
private String name;
private String cardNumber;
private String cvv;
private String dateOfExpiry;
public KAKAOCardStrategy(String nm, String ccNum, String cvv, String expiryDate){
this.name=nm;
this.cardNumber=ccNum;
this.cvv=cvv;
this.dateOfExpiry=expiryDate;
}
@Override
public void pay(int amount) {
System.out.println(amount +" paid using KAKAOCard.");
}
}
class LUNACardStrategy implements PaymentStrategy { // 전략
private String emailId;
private String password;
public LUNACardStrategy(String email, String pwd){
this.emailId=email;
this.password=pwd;
}
@Override
public void pay(int amount) {
System.out.println(amount + " paid using LUNACard.");
}
}
class Item {
private String name;
private int price;
public Item(String name, int cost){
this.name=name;
this.price=cost;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
}
class ShoppingCart {
List<Item> items;
public ShoppingCart(){
this.items=new ArrayList<Item>();
}
public void addItem(Item item){
this.items.add(item);
}
public void removeItem(Item item){
this.items.remove(item);
}
public int calculateTotal(){
int sum = 0;
for(Item item : items){
sum += item.getPrice();
}
return sum;
}
public void pay(PaymentStrategy paymentMethod){ // 행위를 직접 수정하지 않고 교체 가능하도록
int amount = calculateTotal();
paymentMethod.pay(amount);
}
}
public class HelloWorld{
public static void main(String []args){
ShoppingCart cart = new ShoppingCart();
Item A = new Item("kundolA",100);
Item B = new Item("kundolB",300);
cart.addItem(A);
cart.addItem(B);
// pay by LUNACard - 전략이라고 부르는 캡슐화한 알고리즘을 컨텍스트 안에서 바꿔주면서 상호작용
cart.pay(new LUNACardStrategy("kundol@example.com", "pukubababo"));
// pay by KAKAOBank
cart.pay(new KAKAOCardStrategy("Ju hongchul", "123456789", "123", "12/01"));
}
}
/*
400 paid using LUNACard.
400 paid using KAKAOCard.
*/
🙋🏻♀️ 옵저버 패턴
- 주체가 어떤 객체의 상태 변화를 관찰하다가 상태 변화 시 메서드 등을 통해 옵저버 목록에 있는 옵저버들에게 변화를 알려주는 패턴
( 주체란 객체의 상태를 관찰하는 관찰자이며, 옵저버들이란 객체 상태 변화에 따라 전달되는 메서드 등을 기반으로 추가 변경이 생기는 객체들을 의미 )
- 이벤트를 감지하여, 이벤트가 발생할 때마다 미리 정해둔 어떠한 동작을 즉각 수행하게 해주는 프로르개밍 피턴
- 쉬운 예시 : 트위터 , 페이스북? -> 팔로우한 사람이 새로운 글을 올렸을 시! 팔로워에게 알림을~

- 옵저버 패턴은 MVC 패턴에도 주로 사용!
- 위 그림의 예시로, 주체인 Model에서 변경 사항이 생겨 update 메서드로 옵저버인 뷰에 알려주고 이를 기반으로 컨트롤러가 동작
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
interface Subject {
public void register(Observer obj);
public void unregister(Observer obj);
public void notifyObservers();
public Object getUpdate(Observer obj);
}
interface Observer {
public void update();
}
class Topic implements Subject { // 주체 이자 객체
private List<Observer> observers;
private String message;
public Topic() {
this.observers = new ArrayList<>();
this.message = "";
}
@Override
public void register(Observer obj) {
if (!observers.contains(obj)) observers.add(obj);
}
@Override
public void unregister(Observer obj) {
observers.remove(obj);
}
@Override
public void notifyObservers() {
this.observers.forEach(Observer::update);
}
@Override
public Object getUpdate(Observer obj) {
return this.message;
}
public void postMessage(String msg) {
System.out.println("Message sended to Topic: " + msg);
this.message = msg;
notifyObservers();
}
}
class TopicSubscriber implements Observer {
private String name;
private Subject topic;
public TopicSubscriber(String name, Subject topic) {
this.name = name;
this.topic = topic;
}
@Override
public void update() {
String msg = (String) topic.getUpdate(this);
System.out.println(name + ":: got message >> " + msg);
}
}
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Topic topic = new Topic(); // 주체 : 변경사항 탐지
Observer a = new TopicSubscriber("a", topic); //topic의 변경 사항에 따라 변하는 객체
Observer b = new TopicSubscriber("b", topic);
Observer c = new TopicSubscriber("c", topic);
topic.register(a);
topic.register(b);
topic.register(c);
topic.postMessage("amumu is op champion!!");
}
}
/*
Message sended to Topic: amumu is op champion!!
a:: got message >> amumu is op champion!! // 옵저버들이 메세지를 수신받음
b:: got message >> amumu is op champion!!
c:: got message >> amumu is op champion!!
*/
😃 옵저버패턴의 장점
1. 옵저버를 언제들 새로 추가, 제거할 수 있다.
2. 주체와 옵저버는 서로 독립적으로 재사용이 가능하다.
3. 주체나 옵저버가 바뀌더라도 서로에게 영향을 미치지않는다.
4. 객체 사이의 상호 의존성을 최소화 할 수 있다.
'데일리IT🌱' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [ 최단경로 알고리즘 ] 다익스트라 & 플로이드 워셜 (0) | 2023.01.15 |
|---|---|
| 디자인 패턴과 프로그래밍 패러다임_싱글톤 패턴 (0) | 2023.01.04 |
| 오브젝트 _ 코드로 이해하는 객체지향 설계( 3장 ) (0) | 2022.12.09 |
| 오브젝트 _ 코드로 이해하는 객체지향 설계( 1&2장 ) (1) | 2022.12.03 |
| TDD ( Test- Driven - Development ) 에 대하여 (0) | 2022.10.20 |




댓글